
Diagnosis is based on behavior observed by caretakers and, in some cases depending on age, self reports.ĭSM-III. Neither DSM-5 nor ICD-11 list "childhood schizophrenia" as a separate diagnosis. Studies have demonstrated that diagnostic criteria are similar to those of adult schizophrenia. About 50% of young children diagnosed with schizophrenia experience severe neuropsychiatric symptoms. It typically presents after the age of seven. Other symptoms can include irritability, searching for imaginary objects, or low performance. Among the psychotic symptoms seen in childhood schizophrenia non-verbal auditory hallucinations are the most common, and include noises such as shots, knocks, bangs. Delusions are often not systematized and vague. The disorder presents symptoms such as auditory and visual hallucinations, strange thoughts or feelings, and abnormal behavior, profoundly impacting the child's ability to function and sustain normal interpersonal relationships. Differential diagnosis is problematic since several other neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism spectrum disorder, language disorder, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, also have signs and symptoms similar to childhood-onset schizophrenia. Schizophrenia is characterized by positive symptoms that can include hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized speech negative symptoms, such as blunted affect and avolition and apathy, and a number of cognitive impairments.
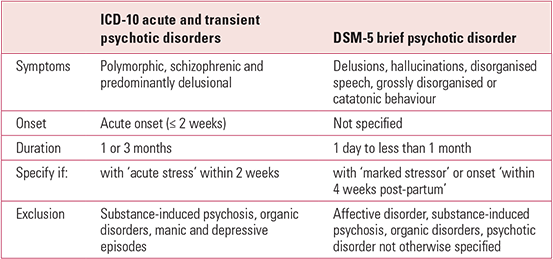
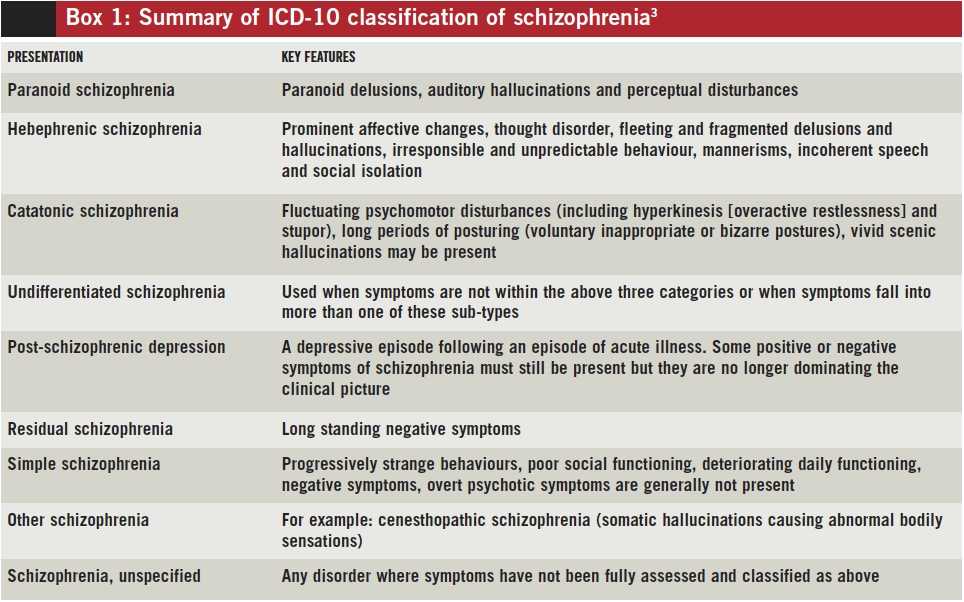
Major depressive disorder or bipolar disorder with psychotic or catatonic features, brief psychotic disorder, delusional disorder, obsessive–compulsive disorder and body dysmorphic disorder, autism spectrum disorder or communication disorders, other mental disorders associated with a psychotic episodeġ⁄ 5 of all forms of psychosis of the schizophrenia spectrum 1.66:1000 among children (0–14 years) Ĭhildhood schizophrenia (also known as childhood-onset schizophrenia, and very early-onset schizophrenia) is similar in characteristics of schizophrenia that develops at a later age, but has an onset before the age of 13 years, and is more difficult to diagnose. Hallucinations, delusions, disorganized behavior or catatonia, negative symptoms (i.e., avolition or reduced affect display) Įpisodic-progredient/shiftlike childhood schizophrenia (malignant, paranoid and slow-progressive sub-types), continuous childhood schizophrenia, recurrent childhood schizophrenia (the rarest form – 5 % of all cases) Medical condition Childhood schizophreniaĬhildhood type schizophrenia schizophrenia, childhood type childhood-onset schizophrenia (COS) very early-onset schizophrenia (VEOS) schizophrenic syndrome of childhoodĬhild psychiatry ( EU), Child and adolescent psychiatry ( USA), clinical psychology


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
